Welcome to BOLD Systems Version 5
Identifying species through DNA barcodes
BOLDv5 features a completely redesigned layout compared to BOLDv4, with a focus on richer content and supporting materials. It also includes a more complex site structure. Tutorials are being developed to facilitate the transition. In the meantime, BOLDv4 remains accessible at v4.boldsystems.org



Data Portal
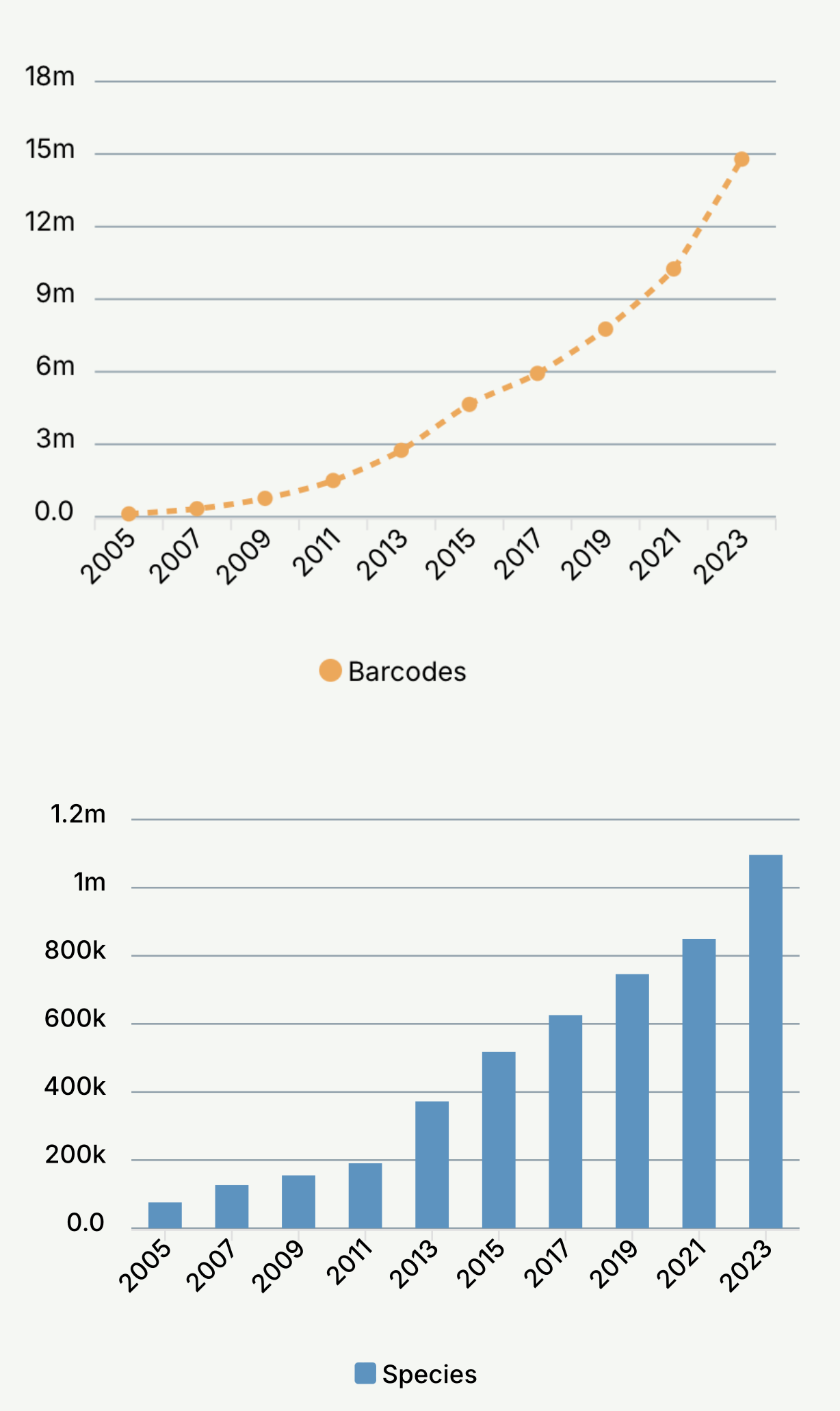
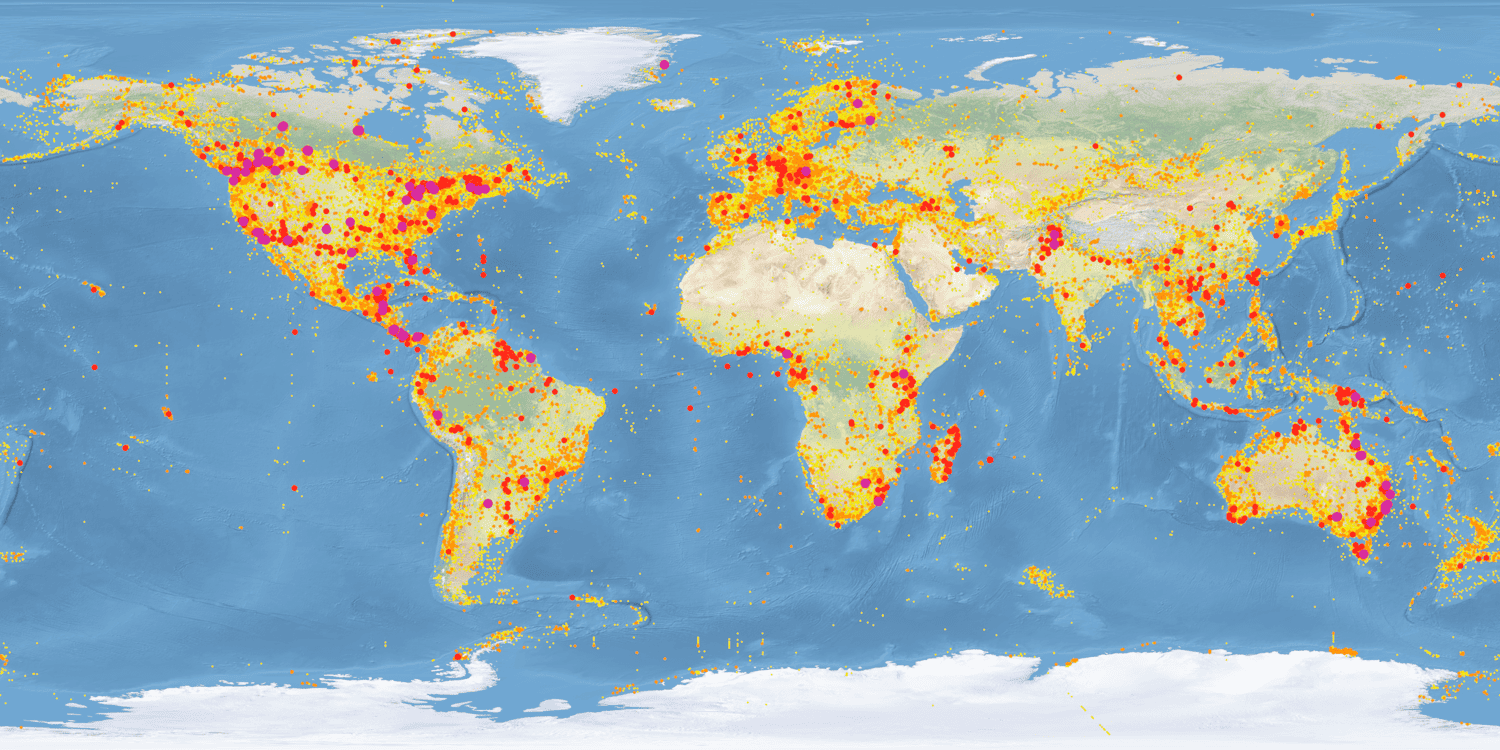
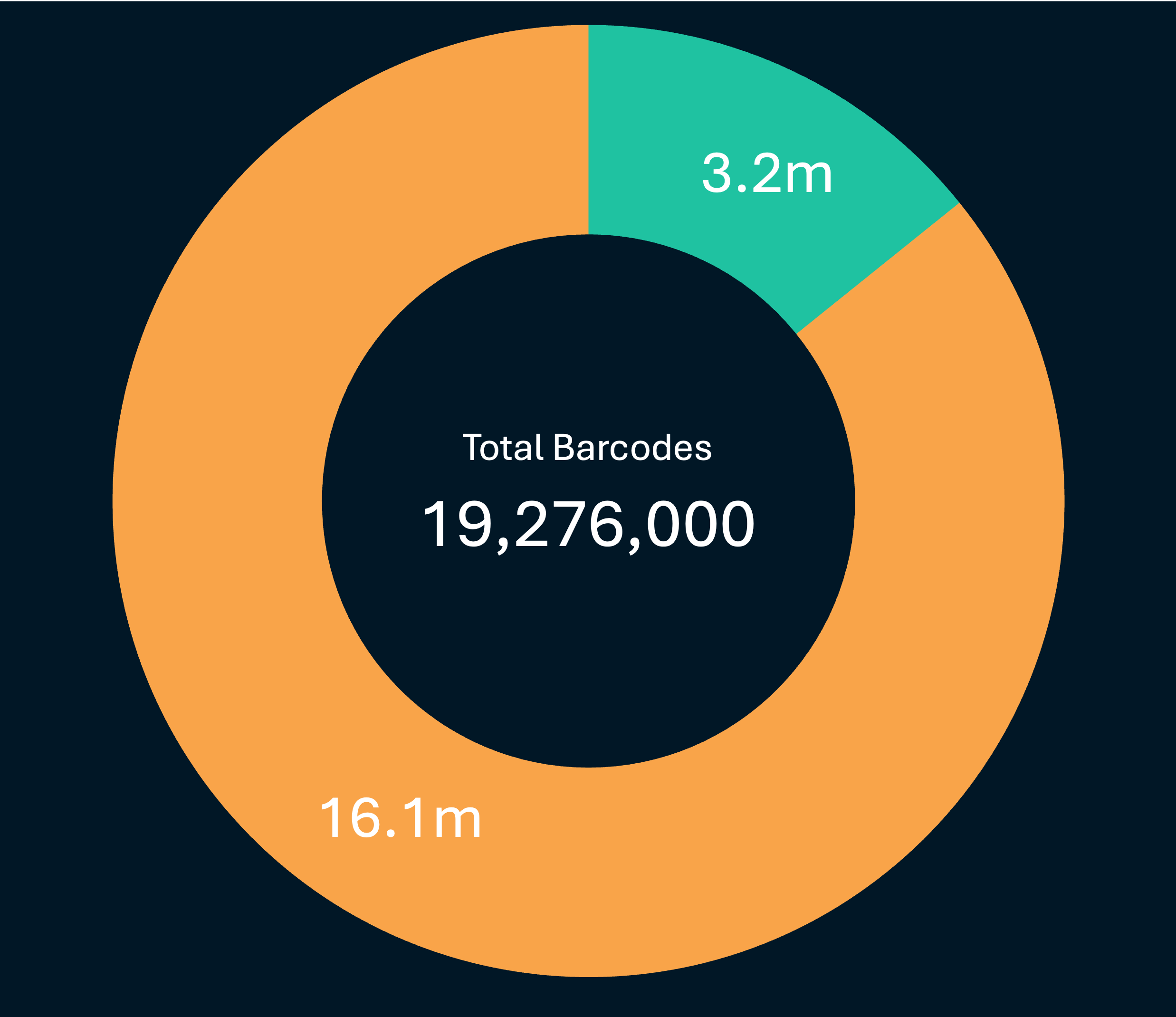
A data portal that provides access to over 16m public records representing 1.1m Species
The records in the portal are public and fully accessible. The remaining records await validation and release.
0
k
BINs
0
k
Animal Species
0
k
Plant Species
0
k
Fungi & Other Species
Overview
Process of identifying species via standardized DNA genetic markers.
01.
DNA Extraction:
The process begins with isolating DNA from the specimen. This step requires care to ensure that the genetic material is free from contaminants and adequately preserved for subsequent analysis.
02.
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction):
Using the extracted DNA, the PCR amplifies target gene regions, creating numerous copies to facilitate detailed examination. This step is crucial for enhancing the visibility of genetic markers necessary for identification.
03.
Sequencing:
The amplified DNA undergoes sequencing, where the order of nucleotides is determined. This sequence represents the unique fingerprint of the species and is essential for accurate identification.
04.
Sequence Matching:
Finally, the obtained sequence is matched against reference libraries in BOLD. This comparison allows for the identification of the specimen by finding the closest records.
Through this method, unknown samples are identified to species present in the reference library.
Data
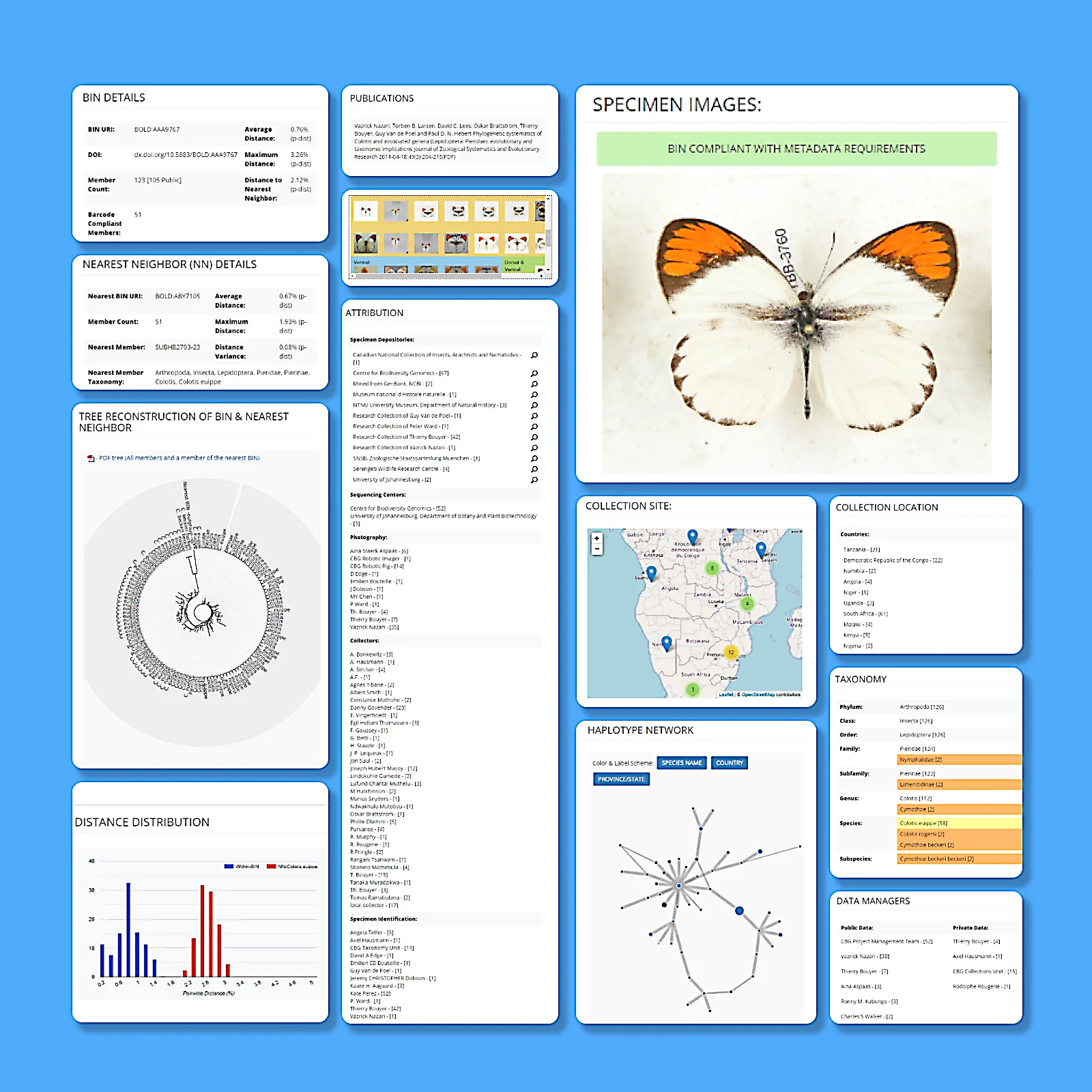
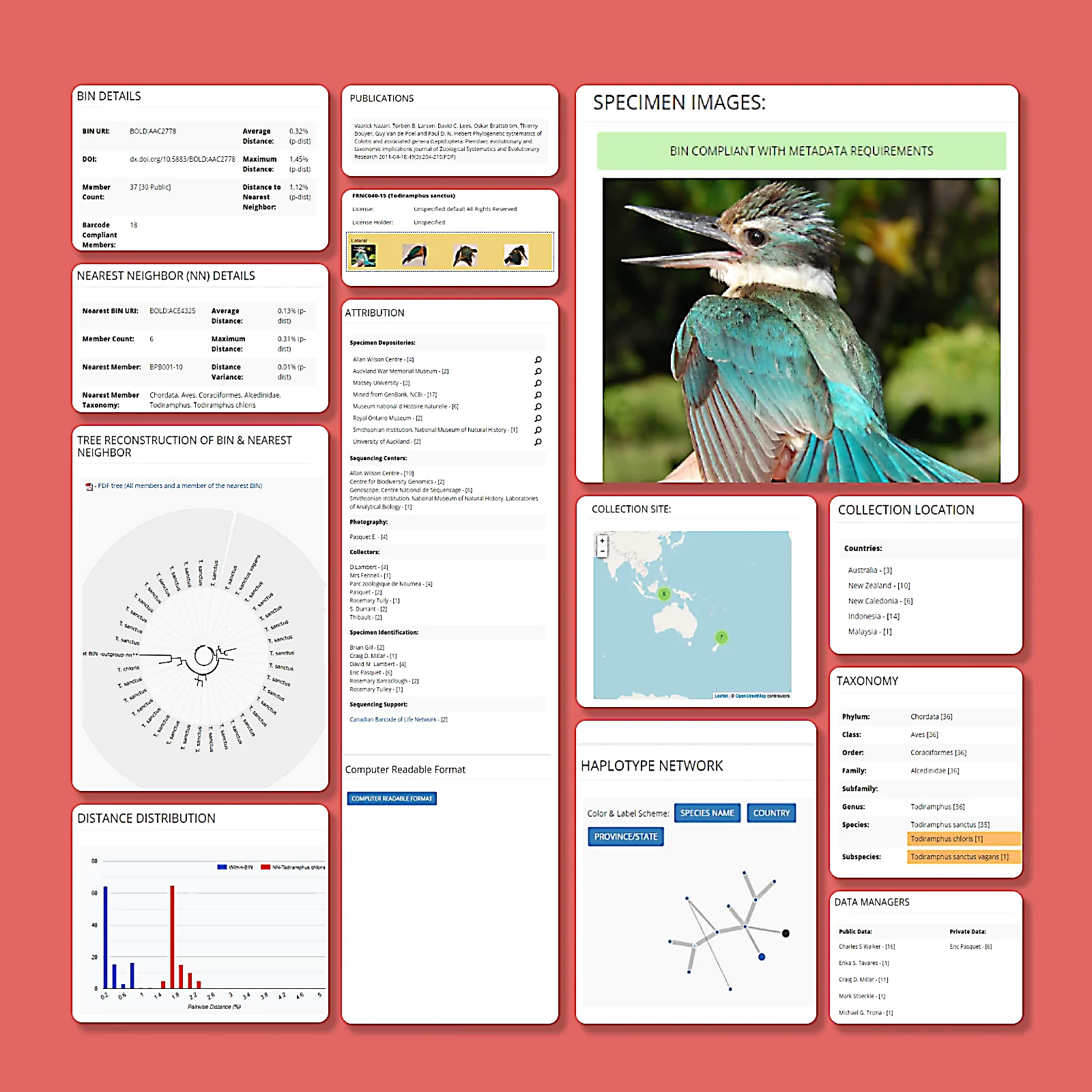
Barcode Index Numbers (BINs)
The Barcode Index Number (BIN) system is an automated method for clustering DNA barcode sequences from animals into operational taxonomic units that usually correspond to species. Each cluster is assigned a unique identifier which serves as a proxy for a species, enabling researchers to examine biodiversity patterns even in the absence of formal species descriptions.
By standardizing DNA-based species identification, the BIN system facilitates large-scale biodiversity assessments, supports species discovery, and enhances ecological and conservation efforts.
Each BIN is linked to a dedicated page that consolidates all available data for its members.
Timeline
The History of BOLD
BOLD started as a database and analytical platform but has since expanded its role. With its rapidly growing database, broad taxonomic coverage, and novel methods and functionalities, it has become a key component of the biodiversity informatics landscape.
Proof-of-concept
BOLD was launched as a proof-of-concept platform at the University of Guelph, designed to manage and disseminate DNA barcode records and standardize DNA barcoding efforts.
2005
Essential tool
BOLD2 introduced functionality to support a global network of early adopters of DNA barcoding. It was accompanied by a publication detailing its storage, management, and analytical capabilities.
2007
Barcode Index Number
BOLD3 introduced the Barcode Index Number (BIN) system, which improved species identification and analysis by organizing similar sequences into distinct clusters and registering them.
2013
Expanded Capabilities
BOLD4 was released with advanced analysis tools, a revamped interface, and expanded marker support.
2016
Global Collaboration and Innovation
BOLD5 introduces a range of new capabilities, including a revamped data model, support for a network of mirrors, new APIs, improved performance.
2024
Growth of Barcodes & Species on BOLD